Limit Cheat Sheet - Limit to infinity properties \mathrm{for}\:\lim_{x\to c}f(x)=\infty, \lim_{x\to c}g(x)=l,\:\mathrm{the\:following\:apply:}. This has the same definition as the limit except it requires xa>. If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there exists c [a, b] with. For a function to be continuous at a point, it must be defined at that point, its limit must exist at the point, and the value of the function at that point. Learn essential calculus limit concepts with our limit cheat sheet. We say lim ( ) xa fx fi =¥ if we can make fx( ) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a). A series that oscilates, for. Simplify complex limit problems with key formulas,. However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist.
Limit to infinity properties \mathrm{for}\:\lim_{x\to c}f(x)=\infty, \lim_{x\to c}g(x)=l,\:\mathrm{the\:following\:apply:}. If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there exists c [a, b] with. However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. Learn essential calculus limit concepts with our limit cheat sheet. Lim ( ) xa fxl fi + =. Simplify complex limit problems with key formulas,. A series that oscilates, for. This has the same definition as the limit except it requires xa>. If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist. We say lim ( ) xa fx fi =¥ if we can make fx( ) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a).
A series that oscilates, for. Learn essential calculus limit concepts with our limit cheat sheet. Lim ( ) xa fxl fi + =. Simplify complex limit problems with key formulas,. If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there exists c [a, b] with. For a function to be continuous at a point, it must be defined at that point, its limit must exist at the point, and the value of the function at that point. We say lim ( ) xa fx fi =¥ if we can make fx( ) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a). However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. Limit to infinity properties \mathrm{for}\:\lim_{x\to c}f(x)=\infty, \lim_{x\to c}g(x)=l,\:\mathrm{the\:following\:apply:}. If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist.
SOLUTION Calculus cheat sheet limits Studypool
If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there exists c [a, b] with. Lim ( ) xa fxl fi + =. Simplify complex limit problems with key formulas,. We say lim ( ) xa fx fi =¥ if we can make fx( ) arbitrarily large (and.
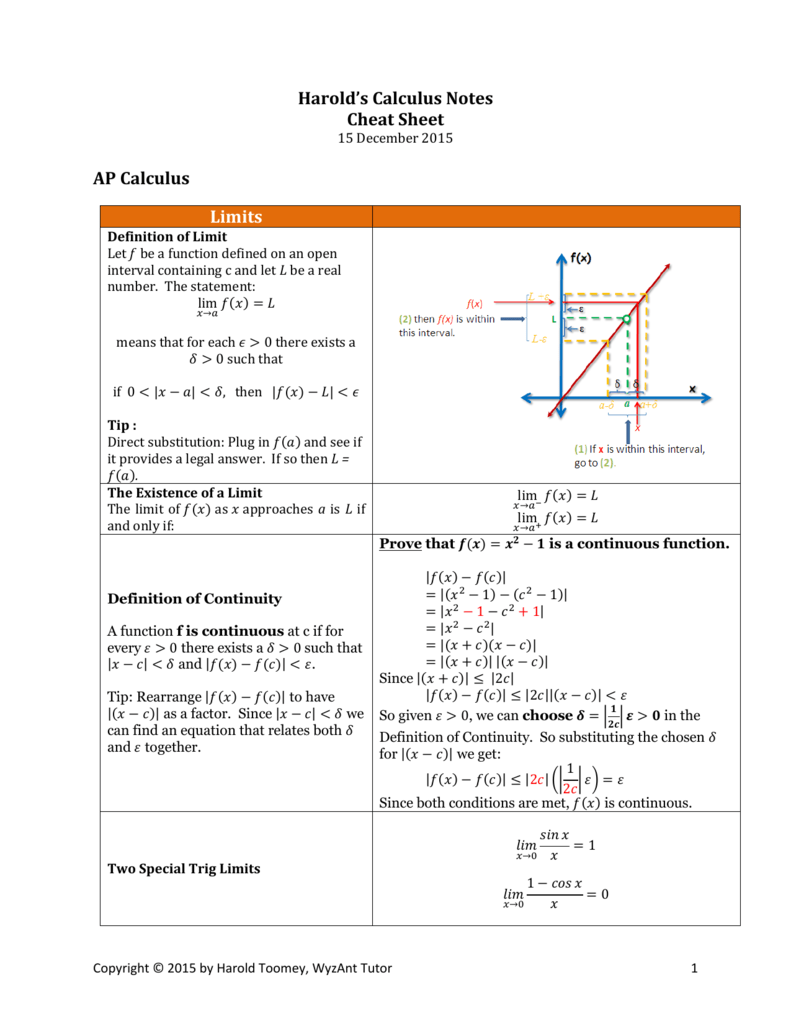
Harold's Calculus Notes Cheat Sheet AP Calculus Limits
If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there exists c [a, b] with. A series that oscilates, for. Limit to infinity properties \mathrm{for}\:\lim_{x\to c}f(x)=\infty, \lim_{x\to c}g(x)=l,\:\mathrm{the\:following\:apply:}. However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. Lim ( ) xa fxl fi + =.
Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits, Derivatives, Integrals Download
Limit to infinity properties \mathrm{for}\:\lim_{x\to c}f(x)=\infty, \lim_{x\to c}g(x)=l,\:\mathrm{the\:following\:apply:}. Simplify complex limit problems with key formulas,. A series that oscilates, for. However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist.
Calculus Cheat Sheet Functions, Limits, Derivatives
Learn essential calculus limit concepts with our limit cheat sheet. This has the same definition as the limit except it requires xa>. However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. A series that oscilates, for. If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist.
Solved Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Precise
For a function to be continuous at a point, it must be defined at that point, its limit must exist at the point, and the value of the function at that point. If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there exists c [a, b] with. Learn.
Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits, Derivatives, Integrals Download
If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist. Lim ( ) xa fxl fi + =. This has the same definition as the limit except it requires xa>. However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there.
SOLUTION Calculus cheat sheet limits Studypool
This has the same definition as the limit except it requires xa>. If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist. Simplify complex limit problems with key formulas,. A series that oscilates, for. However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g.
Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Prec… Calculus, Cheat sheets
A series that oscilates, for. We say lim ( ) xa fx fi =¥ if we can make fx( ) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a). However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. Limit to infinity properties \mathrm{for}\:\lim_{x\to c}f(x)=\infty, \lim_{x\to c}g(x)=l,\:\mathrm{the\:following\:apply:}. This has the same definition as the limit.
Calculus Limits Cheat Sheet Definitions & Evaluation
If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there exists c [a, b] with. For a function to be continuous at a point, it must be defined at that point, its limit must exist at the point, and the value of the function at that point. Learn.
Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits Download Printable PDF Templateroller
However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. We say lim ( ) xa fx fi =¥ if we can make fx( ) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a). Lim ( ) xa fxl fi + =. If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist. Limit to infinity.
For A Function To Be Continuous At A Point, It Must Be Defined At That Point, Its Limit Must Exist At The Point, And The Value Of The Function At That Point.
However, it’s lower/upper bounds might be finite (e.g. Learn essential calculus limit concepts with our limit cheat sheet. This has the same definition as the limit except it requires xa>. Simplify complex limit problems with key formulas,.
Limit To Infinity Properties \Mathrm{For}\:\Lim_{X\To C}F(X)=\Infty, \Lim_{X\To C}G(X)=L,\:\Mathrm{The\:Following\:Apply:}.
We say lim ( ) xa fx fi =¥ if we can make fx( ) arbitrarily large (and positive) by taking x sufficiently close to a (on either side of a). If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] then for any number k between f (a) and f (b), there exists c [a, b] with. Lim ( ) xa fxl fi + =. If this sequence is not convergent, the limit doesn’t exist.